Page 6 - Threading_Handbook
P. 6
1.1 Thread Parameters
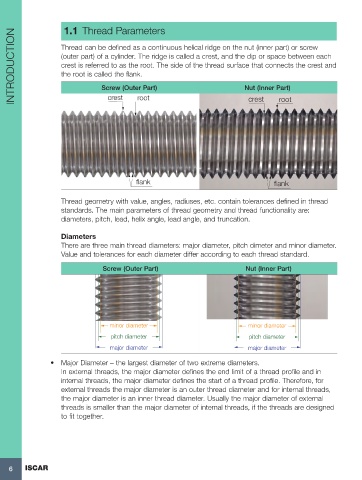
INTRODUCTION Thread can be defined as a continuous helical ridge on the nut (inner part) or screw
(outer part) of a cylinder. The ridge is called a crest, and the dip or space between each
crest is referred to as the root. The side of the thread surface that connects the crest and
the root is called the flank.
Nut (Inner Part)
Screw (Outer Part)
root
crest
crest
root
flank flank
Thread geometry with value, angles, radiuses, etc. contain tolerances defined in thread
standards. The main parameters of thread geometry and thread functionality are:
diameters, pitch, lead, helix angle, lead angle, and truncation.
Diameters
There are three main thread diameters: major diameter, pitch dimeter and minor diameter.
Value and tolerances for each diameter differ according to each thread standard.
Screw (Outer Part) Nut (Inner Part)
minor diameter minor diameter
pitch diameter pitch diameter
major diameter major diameter
• Major Diameter – the largest diameter of two extreme diameters.
In external threads, the major diameter defines the end limit of a thread profile and in
internal threads, the major diameter defines the start of a thread profile. Therefore, for
external threads the major diameter is an outer thread diameter and for internal threads,
the major diameter is an inner thread diameter. Usually the major diameter of external
threads is smaller than the major diameter of internal threads, if the threads are designed
to fit together.
6 ISCAR